Last Updated:
Dubai, United Arab Emirates (UAE)

The most severe rainfall targeted areas north and east of the capital city, Abu Dhabi. (Image: NASA)
UAE hit by unprecedented rainfall, causing widespread flooding. Landsat 9 satellite captures aftermath from space
Unprecedented rainfall flooded parts of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) last week, bringing life to a standstill in Dubai and beyond. The flooding, stemming from the country’s largest deluge on record, was so intense that satellites could still detect it from space days after the rain ceased.
From Tuesday, April 16, through Wednesday, April 17, record rainfall fell in major parts of the country. Notably, Dubai, the country’s most populous city, received a year’s worth of rain in just 12 hours, while areas further east saw nearly two years’ worth within 24 hours. According to CNN, the most severe rainfall targeted areas north and east of the capital city, Abu Dhabi.
Rainfall totals ranged from 4 to 8 inches (about 100 to 200 mm) in most areas, with some locations recording nearly 10 inches (250 mm). Floodwaters surged rapidly and were slow to recede due to the historic deluge, marking the most extreme weather event in the country’s recorded history, spanning 75 years.
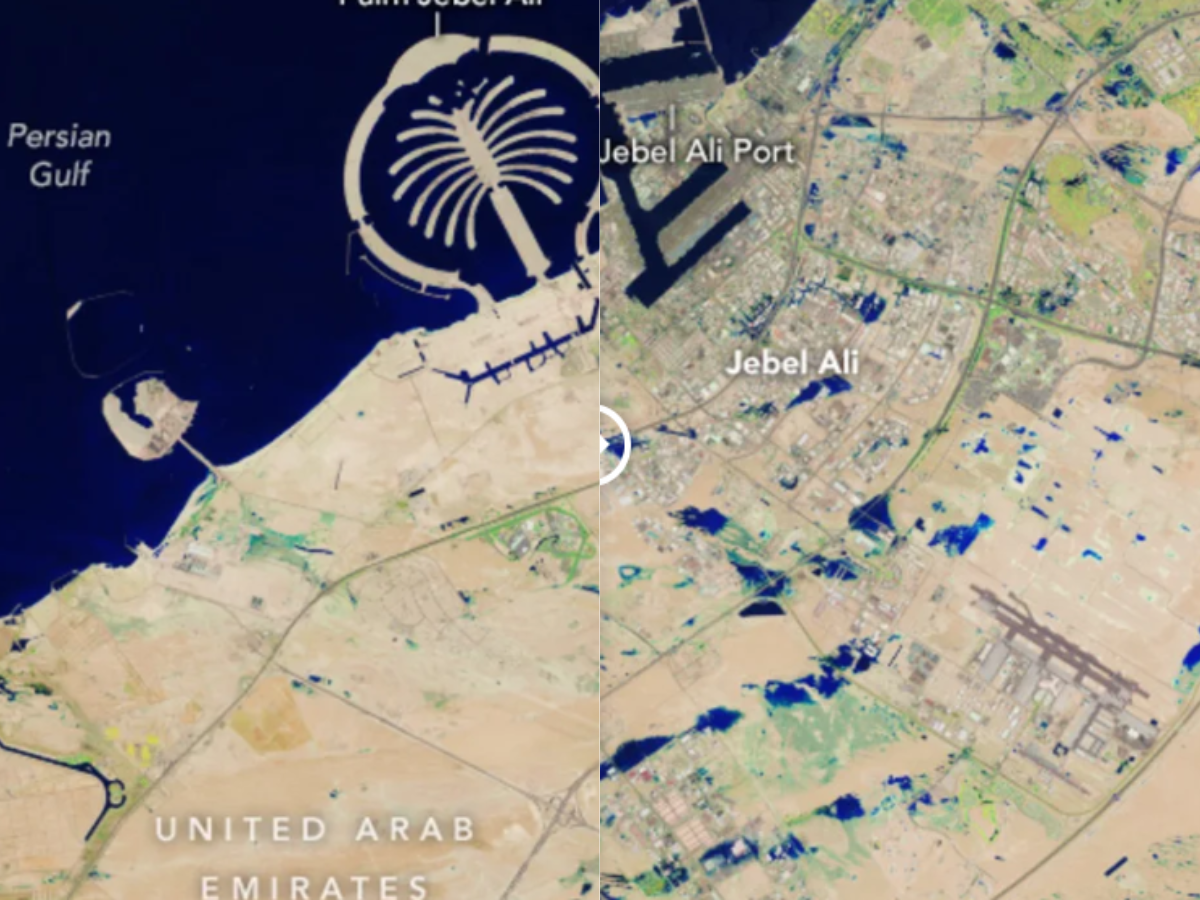
Shortly after the rain subsided, on April 19, the Landsat 9 satellite passed over the UAE, capturing images of lingering floodwaters. Operated by NASA and the United States Geological Survey, Landsat 9’s detailed imagery showcased vast pools of deep blue floodwaters contrasting starkly against the region’s typically arid terrain, particularly in the southernmost portion of Dubai.
Using false colour products, the satellite highlighted the presence of water against the dry ground, with small, shallow bodies appearing light blue and larger, deeper pools appearing dark blue. Moreover, sections of dry ground exhibited a light green tint, indicating residual moisture from the rainfall.
The torrential rain was attributed to a larger storm system traversing the Arabian Peninsula and Gulf of Oman, bringing deadly flooding to nearby Oman. Such extreme rainfall events are increasingly common amid human-driven climate change, as a warmer atmosphere can hold more moisture, resulting in intense rainfall.