The recently enacted Texas Heartbeat Act, a de facto ban on abortion in the Lone Star State, established a system where members of the public could sue abortion providers and advocates for as little as $10,000 if the heart of a fetus was damaged. Abortion is performed after the heartbeat is identified. .
cnxps.cmd.push(function () { cnxps({ playerId: ’36af7c51-0caf-4741-9824-2c941fc6c17b’ }).render(‘4c4d856e0e6f4e3d808bbc1715e132f6’); });
if(window.location.pathname.indexOf(“656089”) != -1){document.getElementsByClassName(“divConnatix”)[0].style.display =”none”;}else if(window.location.pathname.indexOf(“/israel-news/”) != -1){ document.getElementsByClassName(“divConnatix”)[0].style.display = “none”; var script = document.createElement(‘script’); script.src=”https://player.anyclip.com/anyclip-widget/lre-widget/prod/v1/src/lre.js”; script.setAttribute(‘pubname’, ‘jpostcom’); script.setAttribute(‘widgetName’, ‘0011r00001lcD1i_12258’); document.getElementsByClassName(‘divAnyClip’)[0].appendChild(script);}else if(window.location.pathname.indexOf(“/health-and-wellness/”) != -1){ document.getElementsByClassName(“divConnatix”)[0].style.display = “none”; var script = document.createElement(‘script’); script.src=”https://player.anyclip.com/anyclip-widget/lre-widget/prod/v1/src/lre.js”; script.setAttribute(‘pubname’, ‘jpostcom’); script.setAttribute(‘widgetName’, ‘0011r00001lcD1i_12246’); document.getElementsByClassName(‘divAnyClip’)[0].appendChild(script);}
right or wrong, Jerusalem Post Trying to explain the “Heartbeat Act” and what it really means from a medical standpoint for women and babies, with the help of two top doctors: Dr. Benny Chayen, director of Mehadet Services for Women’s Health, and Dr. Ido Salt, director of maternal and fetal medicine at the Rambam health care complex.
1 – When can you hear the fetal heartbeat?
The fetal heartbeat can usually be seen at around six weeks. Hearing the fetal heartbeat is an indication of the viability of the pregnancy.
“At six weeks, all we can say is whether a baby is viable or not viable,” Chayan insisted.
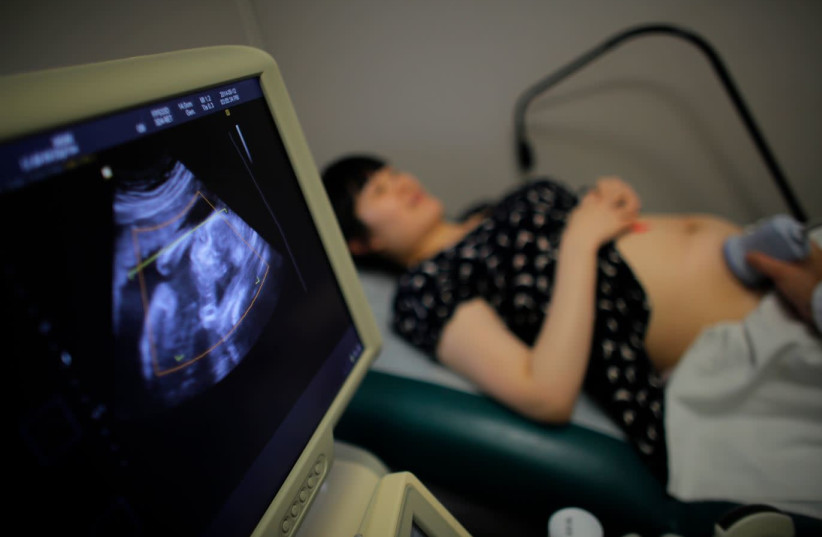 Wu Tianyang, who is five months pregnant with her second child, attends a sonogram at a local hospital in Shanghai on September 12, 2014. (Credit: Carlos Barria / Reuters)
Wu Tianyang, who is five months pregnant with her second child, attends a sonogram at a local hospital in Shanghai on September 12, 2014. (Credit: Carlos Barria / Reuters)
2 – What does the fetus look like at six weeks?
According to Chayen, the size of the fetus at six weeks is not that of a human.
“It looks like a blob of tissue,” he said. “You can’t see a head, a body, or a limb.”
At this stage, the embryo measures at only a few centimeters, Salt said, explaining that the fetus is measured along its longest reach, known as its crown-rump length, or CRL.
3 – How is the gestational age calculated and is it really possible that at six weeks a woman may not even know that she is pregnant?
The gestational age of the fetus is calculated based on the first day of the last menstrual period minus two weeks. So if a woman’s menstruation started eight weeks earlier, the gestational age of the fetus would be six weeks.
Chayen said that if a woman doesn’t have regular cycles or doesn’t know the date of her last period, ultrasound can usually detect the age of the fetus at around six weeks, plus or minus a few days.
Few women, especially those undergoing fertility treatments, are aware of the date of ovulation, which usually occurs around 14 days from the start of one’s period. As such, the gestational age of the period can be calculated from that day.
4 – How soon can one find out if there is a fetal abnormality? When and how are they evaluated?
Salt said the earliest any fetal abnormality can be detected is around 11 weeks, and this would be done through a nuchal translucency scan that shows a collection of fluid under the skin at the back of the neck of the fetus. shows. If this scan shows that there may be some abnormalities, a woman may choose to have an amniocentesis test to check whether the baby has a genetic or chromosomal condition, such as Down syndrome.
Later, at around 14 to 17 weeks and again at around 21 to 24 weeks, the expectant mother may undergo a more detailed ultrasound that may reveal other possible birth defects, such as spina bifida, club feet, cleft lip or even that kidney failure.
In Israel, if malformations are discovered, a woman can terminate her pregnancy even in the third trimester, Chayen said.
5 – In medical terms, when does a fetus become a child?
Usually around 24 weeks, Chayan said, “because that’s the time when a fetus can survive when it’s born.”
He added that at 24 weeks “the baby already has some chance. He will be moved to Neonatal Intensive Care until he is treated there and the baby can survive.”
However, Salt said that definition is beginning to change and is preceded by new technologies that improve the viability of babies born prematurely, such as high-frequency ventilation.
Still, there is usually a “price to be paid” for rescuing these children, he said. Defects may include intra-ventricular hemorrhage, bleeding in or around the ventricles in the brain; serious eye problems; Or even respiratory distress syndrome, Salt said.
6 – And what is a fetus?
The pre-embryo state is embryonic — “it’s just a few cells,” Cheon said, noting that the fetus is usually called that way in the first one to two weeks of pregnancy.
7 – What abortion methods are available in Israel?
There are two types of legal abortion in Israel: surgical and pharmaceutical.
A surgical abortion is usually performed between 11 and 14 weeks and involves “vacuum aspiration,” whereby the doctor will numb a woman’s cervix and then essentially expel the contents of the uterus, Salt said. said.
With the pharmaceutical approach, if there is a normal pregnancy and a woman wants to end it, the doctor will first prescribe an anti-progesterone drug that blocks the progesterone hormone, which supports early pregnancy and usually causes miscarriage. causes. After about 48 hours, Salt explained, the woman would then be given a second drug, usually Cytotec, which “orders the uterus to evaluate for pregnancy.”
Under Israeli law there are four conditions by which a woman is legally allowed to terminate a pregnancy:
1: If a woman is below the legal age (18) to marry or is above 40 years.
2: If a woman becomes pregnant by someone other than her husband, for example in the case of rape, incest or adultery or if she is not married.
3: If the child will be born with a genetic abnormality.
4: If the mother is suffering from any physical or mental condition which may endanger her life.
8 – Can a woman have medical conditions that require her to have an abortion?
“A woman may have medical problems such as heart or kidney problems, and pregnancy may worsen the condition,” Chayen said. “In these cases, a doctor may recommend an abortion.”
Other examples may include women with multiple sclerosis.
“A woman deteriorates much faster than a woman without pregnancy. But the woman may decide that she wants the baby and should not terminate the pregnancy, even if it threatens her,” he said.
To have an abortion in Israel, a woman has to explain herself to a committee. By week 23, she appears before a standards committee consisting of two doctors and a social worker. According to Salt, over 99% of abortion requests performed in the first trimester are approved.
There are around 40 such committees in hospitals and other medical centers across the country.
Salt said that from the 24th week, a special committee of five members would be convened to discuss the application.
“You have to prove that there is a serious abnormality in the fetus that will cause the child to be more than 30 percent severely disabled before the committee will approve termination of the pregnancy after 24 weeks,” he said.
Although he also added that “we don’t know about all abortions and some are done without the approval of these committees.”
9 – How many abortions are performed per year in Israel?
In Israel, according to Salt, about 20,000 abortions are performed each year, 10% of the number of stillbirths, which is about 200,000.
10 – Could there ever be a Texas Heartbeat Act in a Jewish state?
Doctors had only one answer to that question: As in Texas, it is not a question of health but of politics.